分布式计算框架: Ray #
Ray 是一个开源的框架, 用于规模化 AI 与 Python 应用. 它提供了一个统一的 API 用于构建分布式应用.
为什么选择 Ray? #
这里引用官方的一段话:
Today’s ML workloads are increasingly compute-intensive. As convenient as they are, single-node development environments such as your laptop cannot scale to meet these demands.
Ray is a unified way to scale Python and AI applications from a laptop to a cluster.
With Ray, you can seamlessly scale the same code from a laptop to a cluster. Ray is designed to be general-purpose, meaning that it can performantly run any kind of workload. If your application is written in Python, you can scale it with Ray, no other infrastructure required.
Ray 是一种统一的方式,可以将 Python 和 AI 应用从笔记本电脑扩展到集群。
如今的机器学习工作负载计算量日益增加。尽管单节点开发环境方便,但像你的笔记本电脑这样的单节点开发环境无法满足这些需求。
有了 Ray,你可以无缝地将同一批代码从笔记本扩展到集群。 Ray 设计为通用型,意味着它可以高效运行任何类型的工作负载。如果你的应用是用 Python 编写的,可以用 Ray 扩展,不需要其他基础设施。
Ray 在 ML infra 中扮演的角色 #
在 ML Infra 中,Ray 让复杂、多样、异构的 ML 计算,以统一、可扩展、可调度的方式运行在集群上。
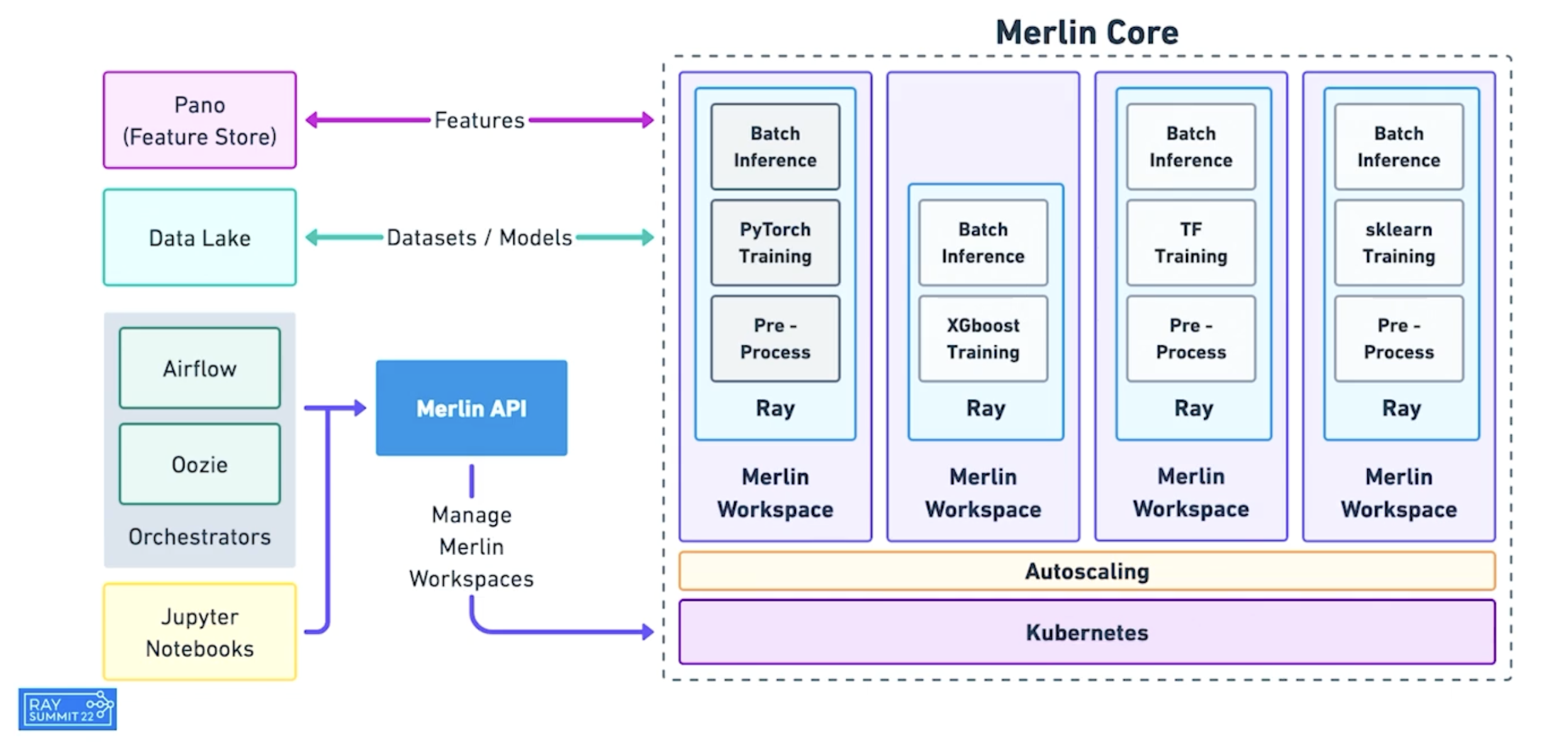
例如, Shopify 的 Merlin 利用 Ray 自动调度计算任务到集群上.
Ray 调度对象 #
Ray 的核心功能是自动调度计算负载. 调度的对象包括两种: Task 与 Actor.
Task #
Task 顾名思义就是任务. 它代表无状态的工作负载. 以官方的示例为例:
import ray
ray.init()
@ray.remote
def f(x):
return x * x
futures = [f.remote(i) for i in range(4)]
print(ray.get(futures)) # [0, 1, 4, 9]
在加上 @ray.remote 之后, f 就成了一个可以被远程运行的 Task.
Ray 调度器会自动决定将这个 Task 运行在哪个节点上.
值得一提的是, Task 是可以指定资源需求的. 例如这个 Task 会运行在不少于 4 核 CPU 与 2 个 GPU 的节点上:
@ray.remote(num_cpus=4, num_gpus=2)
def my_function():
return 1
Actor #
而 Actor 则代表有状态的工作负载. 以官方的示例为例:
import ray
ray.init()
@ray.remote
class Counter:
def __init__(self):
self.value = 0
def increment(self):
self.value += 1
return self.value
def get_counter(self):
return self.value
# Create an actor from this class.
counter = Counter.remote()
例如, 一个典型的应用场景是模型推理. 这种场景下我们希望加载一次,反复推理. 如果使用 Task 的话每次都要重新 load.