MIT 6.5840 Lab 记录 #
学习一下 Golang 与分布式系统.
课程地址: https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.824/index.html
我用的是 2025 Spring 的 Lab. 最后一个 Lab 没有做.
Lab 1 - MapReduce #
第一个实验是经典的 MapReduce. 但是需要用 Golang 实现. 我很久以前在学校的操作系统实验课 (基于 OSTEP) 上做过一个. 但是细节已经忘的差不多了.
算法 #
网上找到了两幅示意图, 用来描述 MapReduce 算法的过程.
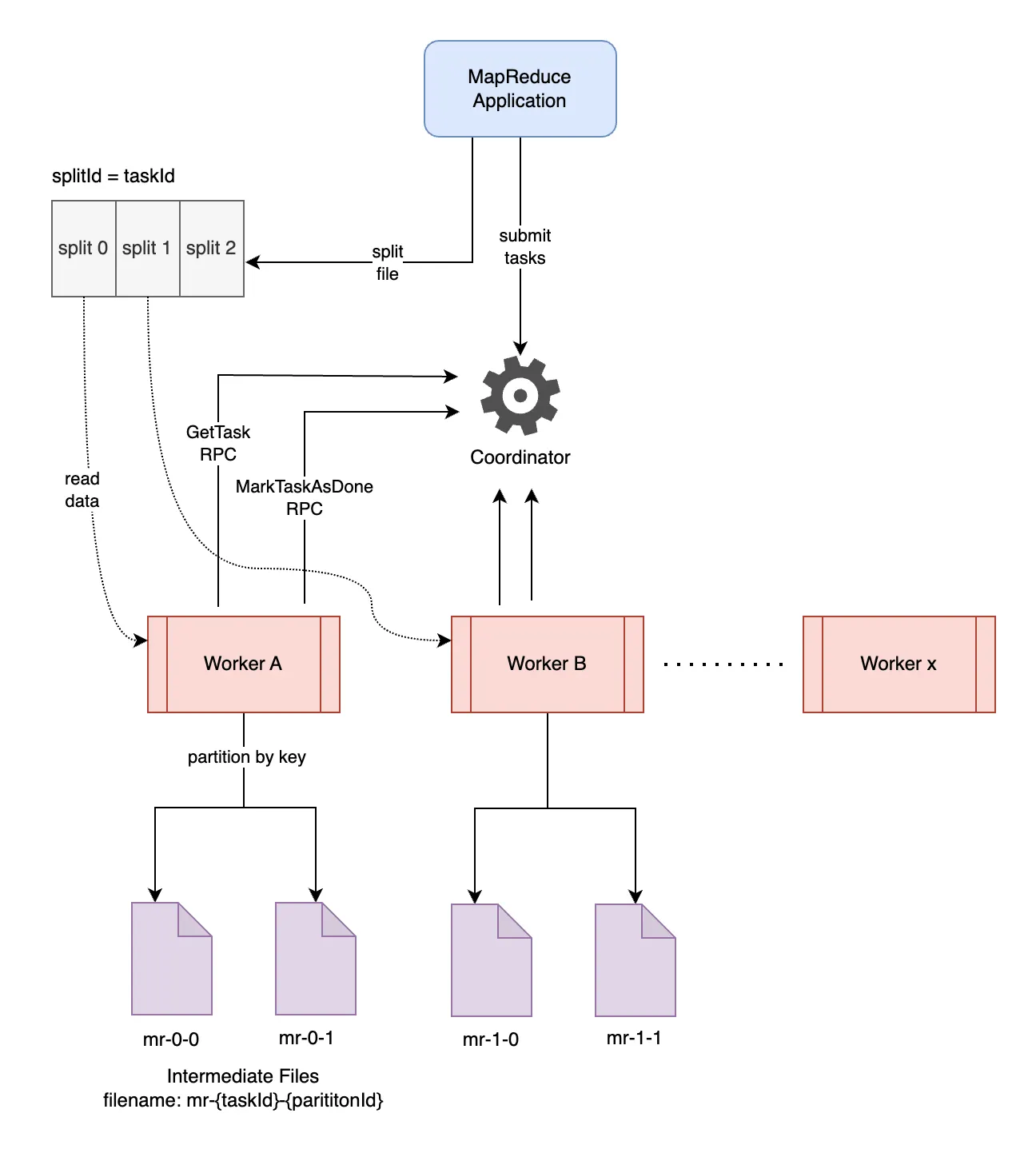
Map 阶段的目的是将原始输入分成键值对, 并且分到一个类似哈希表的结构中 (Reducer 的数量就对应哈希表的桶的数量), 确保同样的 Key 分到同样的桶中 (这一步也叫做 Partition).
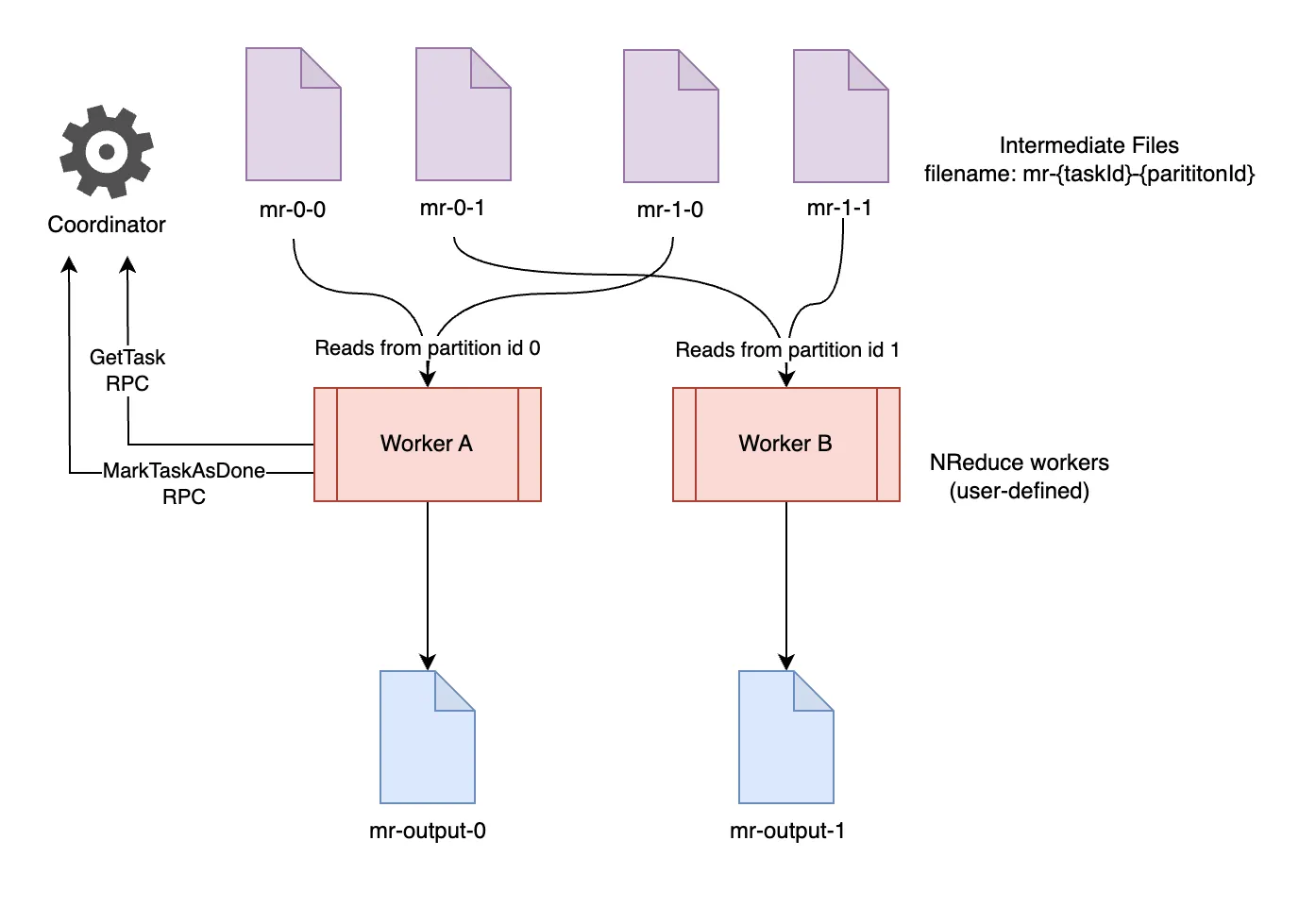
Reduce 阶段的目的是挨个处理哈希表的每个桶里面的数据并进行汇总。
实现 #
MapReduce 集群中运行的节点分为控制节点 (Coordinator) 与工作节点 (Worker). 其中工作节点通过 RPC 从控制节点获取任务并执行.
Worker 节点启动后不断通过 RPC 向 Coordinator 节点询问任务, 如果获取到就执行. 执行完毕后通知 Coordinator 节点该任务已完成.
Coordinator 节点启动之前会先根据输入创建对应的任务, 创建完毕后启动 RPC, 通过 RPC 向 Worker 节点下发任务. 这里注意的是 RPC 可能存在线程安全问题, 需要上锁.
Lab 2 - Key/Value Server #
第二个实验是键值对服务器. 某种程度上跟 redis 这种数据库有点相似.
第一个任务是编写 Put 跟 Get 方法. 没什么好说的, 按部就班实现就可以.
第二个任务需要用上一步写的 Put 与 Get 实现一个锁. 这里踩了一个坑, 最开始的实现没注意到每个 go routine 里面的 lock 都是单独 make 的而不是共享的. 结果卡了半天. 正确的实现如下:
func MakeLock(ck kvtest.IKVClerk, l string) *Lock {
lk := &Lock{ck: ck, key: l}
lk.ck.Put(l, "unlocked", 0) // Initialize the lock state to "unlocked"
// You may add code here
return lk
}
func (lk *Lock) Acquire() {
for {
val, ver, _ := lk.ck.Get(lk.key)
if val == "unlocked" {
err := lk.ck.Put(lk.key, "locked", ver)
if err == rpc.OK {
return
}
}
}
}
func (lk *Lock) Release() {
_, ver, _ := lk.ck.Get(lk.key)
lk.ck.Put(lk.key, "unlocked", ver)
}
第三个任务按部就班实现就可以.
第四个任务是在第三个的基础上实现第二个任务. 这里只需要让每个线程上锁时采用不同的值即可.
func (lk *Lock) Acquire() {
for {
val, ver, _ := lk.ck.Get(lk.key)
if val == "unlocked" {
new_val := kvtest.RandValue(8)
lk.ck.Put(lk.key, new_val, ver)
val, _, _ := lk.ck.Get(lk.key)
if val == new_val {
return
}
}
}
}
Lab 3 - Raft #
先写点小代码用来打印日志, 方便 debug.
func (rf *Raft) peekInfo() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("rf %d, term: %d, state: %v, lastLogIndex: %v, lastLogTerm: %v, commitIndex: %v, log: %v", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, rf.state, rf.lastLogIndex, rf.lastLogTerm, rf.commitIndex, peekLog(rf.log))
}
func peekLog(log []Entry) []Entry {
terms := make([]int, len(log))
for i, entry := range log {
terms[i] = entry.Term
}
return log
}
// 用于重定向日志输出到文件
// 把下面的插入到 raft 测试函数的开头
filename := time.Now().Format("2006-01-02T15:04:05") + ".log"
file, err := os.OpenFile(filename, os.O_CREATE|os.O_WRONLY|os.O_APPEND, 0644)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("unable to open log: %v", err)
}
defer file.Close()
log.SetOutput(file)
Part 3A: leader election #
第一个任务是实现领导者选举. 按照 Raft 算法的内容, 实现思路如下:
每个 Raft 对象维护唯一一个运行的 goroutine. 这个 goroutine 对应着 Raft 的计时器. 会不断循环.
对于 Follower 而言, goroutine 需要做的如下:
- 检查在 sleep 时是否收到过 heartbeat
- 如果没收到则认为超时, 切换为 Candidate
- 如果收到了则更新计时器. (通过 sleep 设置计时器, 到时间 wakeup)
对于 Candidate 而言, goroutine 需要做的如下:
- 发起投票 (非阻塞的)
- 发起投票的 RPC 函数会处理投票结果, 如果发现得到了过半认同则切换为 Leader.
- 设置计时器 (通过 sleep 设置计时器, 到时间 wakeup)
对于 Leader 而言, goroutine 需要做的如下:
- 发送心跳
- 设置计时器 (通过 sleep 设置计时器, 到时间 wakeup)
对于计时器时间的选择如下:
- Leader 的计时器设置为 100 ms.
- 这是因为 Lab 给出的限制是 Leader 每秒最多广播 10 次
- Follower 与 Candidate 的计时器设置为 150 ~ 300 ms.
- 这是确保两次唤醒之间至少能收到一次心跳
实现如下:
doFollower,doCandidate与doLeader对应三个角色下的 goroutine.- 切换角色时会启动新的 goroutine, 原来的 goroutine 检查到角色不对时会自动退出.
- routineNum 用于维护唯一的 goroutine.
- 这里踩了个坑, 单纯用 state 来判断是否退出原来的 goroutine 是有问题的
- 比如从 follower -> candidate -> follower 会导致同时存在两个 follower goroutine.
- 而多个 goroutine 会导致运行结果出错.
- 因此需要一个 routineNum 来确保当前的 routine 是唯一的.
运行结果
raft1 % go test -v -run 3A
=== RUN TestInitialElection3A
Test (3A): initial election (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 58 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestInitialElection3A (3.03s)
=== RUN TestReElection3A
Test (3A): election after network failure (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 136 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestReElection3A (4.56s)
=== RUN TestManyElections3A
Test (3A): multiple elections (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.4s #peers 7 #RPCs 648 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestManyElections3A (5.41s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 13.539s
Part 3B: log #
接下来的任务是实现日志的存储, 论文的算法大致如下:
对于 Leader:
- 维护
nextIndex与matchIndex两个数组 - 每次发送心跳时给编号为
i的 peer 发送log[nextIndex[i]:]的日志.- 如果
nextIndex[i]==lastLogIndex则发送的日志内容为空
- 如果
- 如果对面接收了
- 将
nextIndex[i]设为nextIndex[i]加上刚才发送日志的长度 - 将
matchIndex[i]设为nextIndex[i] - 1 - 如果
matchIndex[i]比commitIndex要大, 并且log[matchIndex[i]].Term == currentTerm:- 检查是否有过半的 peer 达到了这个
matchIndex - 如果有的话, 更新
commitIndex
- 检查是否有过半的 peer 达到了这个
- 将
- 如果对面没接收
- 将
nextIndex[i]减 1
- 将
- 维护
对于 Follower:
- 对于接收到的日志:
- 检查
PrevLogIndex位置上的 term 是否等于LastLogTerm - 如果等于
- 说明匹配上了, 把发来的日志加上
- 根据发来的
LeaderCommit更新自己的commitIndex
- 如果不等于
- 说明没匹配上, 返回
Success为 False
- 说明没匹配上, 返回
- 检查
- 对于接收到的日志:
除此以外, 一个可以优化的点是, 如果对面没接收日志, 可以跳跃性的减少 nextIndex[i] 而不是单纯减 1. 可以设置两个返回值: ConflictTerm 与 ConflictIndex
ConflictTerm用于指示 Follower 在PrevLogIndex位置上的 TermConflictIndex用于指示ConflictTerm最早出现的位置(或该 Term 不存在时,给出首个大于PrevLogIndex的位置)
这样 Leader 就可以根据这两个值直接向前跳转而不是单纯减 1.
运行结果
raft1 % time go test -run 3B
Test (3B): basic agreement (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 0.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 16 #Ops 0
Test (3B): RPC byte count (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 48 #Ops 0
Test (3B): test progressive failure of followers (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 144 #Ops 0
Test (3B): test failure of leaders (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.9s #peers 3 #RPCs 186 #Ops 0
Test (3B): agreement after follower reconnects (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 136 #Ops 0
Test (3B): no agreement if too many followers disconnect (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.5s #peers 5 #RPCs 396 #Ops 0
Test (3B): concurrent Start()s (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 0.7s #peers 3 #RPCs 14 #Ops 0
Test (3B): rejoin of partitioned leader (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 1076 #Ops 0
Test (3B): leader backs up quickly over incorrect follower logs (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 26.7s #peers 5 #RPCs 15612 #Ops 0
Test (3B): RPC counts aren't too high (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 40 #Ops 0
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 58.477s
go test -run 3B 1.68s user 0.65s system 3% cpu 59.048 total
Lab 3 的 Hint 中提到过两点:
- Leader 每秒发送的心跳不能超过十次.
- 尽量保持 3B 实验运行用时不超过 60s 并且 CPU 时间不超过 5s (否则后续实验可能超时)
但是测试发现, 如果提高 Leader 发送心跳的间隔, 会显著导致运行用时变慢. 最终我设置 Leader 发送心跳间隔为 100ms, 这样最终的运行时间就卡着 60s 的边界. 如果降低心跳间隔, 运行时间还可以再降, 但这样就违背了第一条.
Part 3C: persistence #
对于 Raft 的持久化参考论文中的 Figure 2 就可以. 需要持久化的值包括 currentTerm, votedFor 与 log. 当这三个值有修改的时候就同步更新 Persister 存储的值. 启动时从 Persister 中加载这些值, 并根据值重建其他的变量 (如 lastLogIndex 与 lastLogTerm).
这里碰到了一个问题, 对于 Figure 8 unreliable 的测试有时候会达不成 Agreement. 猜测是因为用时太久导致的. 调低了心跳间隔到 10ms 以后就通过了. (但是这也违背了 Lab 的要求:Leader 每秒发送的心跳不能超过十次.) 这里也不得不说这个 Corner Case 太过于刁钻. 由于暂时想不到什么解决方案, 我就先忽略了 Lab 的这个要求, 进行了下个 Part.
后来我才发现了用时过久的原因. 问题出在
RequestVote这个 RPC 上.当 Follower 第一次对某个 Term 投下赞成票的时候, 应该视作收到了一次心跳.
否则的话, 会导致不停的选举.
运行结果
raft1 % go test -run 3C
Test (3C): basic persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 72 #Ops 0
Test (3C): more persistence (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 13.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 384 #Ops 0
Test (3C): partitioned leader and one follower crash, leader restarts (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 36 #Ops 0
Test (3C): Figure 8 (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 31.9s #peers 5 #RPCs 1004 #Ops 0
Test (3C): unreliable agreement (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 5.9s #peers 5 #RPCs 244 #Ops 0
Test (3C): Figure 8 (unreliable) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 35.4s #peers 5 #RPCs 3460 #Ops 0
Test (3C): churn (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 792 #Ops 0
Test (3C): unreliable churn (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.5s #peers 5 #RPCs 732 #Ops 0
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 125.297s
Part 3D: log compaction #
最后一个实验是进行日志压缩. 当上层服务不需要某些日志的时候, 可以压缩为 Snapshot. 算法参考原论文, 写的比较详细.
这里提一下论文没有提到的一个点: 什么时候调用 InstallSnapshot 这个 RPC:
- 当 Leader 发现某个 peer 的
nextIndex已经到达自己的lastIncludedIndex的时候 (也就是落后自己太多)
剩下的就是一些切片判断越界, index 互相转化的操作.
运行结果
raft1 % go test -run 3D
Test (3D): snapshots basic (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 150 #Ops 0
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 47.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 2066 #Ops 0
Test (3D): install snapshots (disconnect) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 59.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 2586 #Ops 0
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 27.3s #peers 3 #RPCs 1000 #Ops 0
Test (3D): install snapshots (crash) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 31.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 1104 #Ops 0
Test (3D): crash and restart all servers (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 244 #Ops 0
Test (3D): snapshot initialization after crash (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 82 #Ops 0
PASS
ok 6.5840/raft1 178.648s
Lab 4 - Fault-tolerant Key/Value Service #
接下来就是基于前面的 Raft 框架搭一些东西.
Part A: replicated state machine (RSM) #
第一个任务是实现 RSM, 也就是复制状态机. 其实就是给 Raft 设计一套上层的接口.
对于 RSM 而言, 第一个需要实现的功能是从 Raft 那里拿到需要 apply 的日志并进行 apply. 这就需要一个协程来干这个工作, 不断的从 applyCh 中尝试读取需要 apply 的日志并进行 apply.
第二个需要实现的功能就是提交日志, 也就是 Submit 函数, 通过这个函数向 Raft 提交日志.
作为一个共识算法, Raft 会被部署在很多台机器上, 每台机器都有一个 Raft 服务. 每个 Raft 服务都会对应一个 RSM. 应用在提交日志的时候, 会先找到一台是 Leader 的机器, 然后提交到这台机器上, 由这台机器跟其他机器达成共识.
流程大概如下:
- 客户端调用 Leader 机器上的
rsm.Submit函数, 尝试提交日志 rsm.Submit调用raft.Start尝试提交日志, 然后等着- 如果当前还是 Leader 并且 Term 也没变, 说明还在达成共识中.
- 如果自己尝试提交的日志被 commit 了, 那就告诉客户端添加成功了.
- 如果 Leader 地位没了 / Term 变了, 那就说明可能没提交成功, 为了避免无意义的等待, 就直接认为没提交成功.
为了区分 applyCh 传来的 commit 的日志是不是自己提交的那一份, 还需要再给日志封装一层, 也就是 Op, 通过 Op.Me 与 Op.Id 来判断是不是自己提交的那一条日志.
这里踩了个坑, 用时间戳来当Op.Id是有问题的, 因为精度不够, 并发提交会出现相同的Op.Id. 换用生成 64 位随机数就好了.
除此以外, 为了能让 rsm.Submit 知道自己提交的日志有没有 commit, 还需要给 RSM 添加一个哈希表. Key 是 Op.Id, Value 为 RSM apply 的返回值, 初始化为 nil. 这样 rsm.Submit 就可以通过轮询的方式查询自己提交的日志有没有 commit.
运行结果
rsm % go test -v -run 4A
=== RUN TestBasic4A
Test RSM basic (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 44 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestBasic4A (2.35s)
=== RUN TestConcurrent4A
Test concurrent submit (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 0.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 8 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestConcurrent4A (0.59s)
=== RUN TestLeaderFailure4A
Test Leader Failure (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.4s #peers 3 #RPCs 42 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestLeaderFailure4A (1.44s)
=== RUN TestLeaderPartition4A
Test Leader Partition (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.1s #peers 3 #RPCs 64 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestLeaderPartition4A (2.07s)
=== RUN TestRestartReplay4A
Test Restart (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 22.6s #peers 3 #RPCs 428 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRestartReplay4A (22.64s)
=== RUN TestShutdown4A
Test Shutdown (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 10.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 0 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestShutdown4A (10.00s)
=== RUN TestRestartSubmit4A
Test Restart and submit (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 33.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 438 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestRestartSubmit4A (33.24s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/kvraft1/rsm 72.769s
Part B: Key/value service without snapshots #
第二个任务就是在第一个任务创建的 RSM 的基础上再包一层 RPC 调用 (kvserver) 并且提供一个接口 (Clerk) 用来 Get 与 Put.
对于客户端, 会调用 Clerk 的 Get 与 Put. Clerk 逐个联系 kvserver 尝试 RPC 调用 kvserver 上的 Get 与 Put.
- 如果这个 kvserver 正好是 Leader, 那就执行对应的操作.
- 如果不是, 就告诉 Clerk 找错了. Clerk 会再询问其他 kvserver.
这里有两个地方的逻辑需要注意:
- 在 Leader 机器执行
Put请求的时候, 如果 Leader 机器没能在一个 Follower 超时时间内完成 commit, 那么大概率是联系到了一个已经被孤立出去的 Leader, 应该视作追加失败并返回ErrWrongGroup. - 在 Leader 机器执行
Put请求的时候, 其 Raft 模块应该在接到请求以后立即广播一个AppendEntities而不是等下一次心跳的时候再广播. 否则会造成不必要的等待导致Put速度过慢.
还有一个小坑需要注意一下, 给 Raft 创建的 applyCh 空间一定要开大点, 因为 golang 的 channel 在满了以后是会阻塞的, 有概率会造成死锁. 我最开始的时候设置的 100, 在某个测试的时候就死锁了. 改到 1000 就可以通过.
运行结果
kvraft1 % go test -v -run 4B
=== RUN TestBasic4B
Test: one client (4B basic) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 5902 #Ops 1153
--- PASS: TestBasic4B (3.21s)
=== RUN TestSpeed4B
Test: one client (4B speed) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.2s #peers 3 #RPCs 3032 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSpeed4B (1.24s)
=== RUN TestConcurrent4B
Test: many clients (4B many clients) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 3.3s #peers 5 #RPCs 6440 #Ops 1251
--- PASS: TestConcurrent4B (3.32s)
=== RUN TestUnreliable4B
Test: many clients (4B many clients) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.0s #peers 5 #RPCs 2176 #Ops 351
--- PASS: TestUnreliable4B (3.95s)
=== RUN TestOnePartition4B
Test: one client (4B progress in majority) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.8s #peers 5 #RPCs 146 #Ops 3
Test: no progress in minority (4B) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.1s #peers 5 #RPCs 143 #Ops 3
Test: completion after heal (4B) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 1.5s #peers 5 #RPCs 105 #Ops 4
--- PASS: TestOnePartition4B (4.46s)
=== RUN TestManyPartitionsOneClient4B
Test: partitions, one client (4B partitions, one client) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 9.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 6599 #Ops 1235
--- PASS: TestManyPartitionsOneClient4B (9.23s)
=== RUN TestManyPartitionsManyClients4B
Test: partitions, many clients (4B partitions, many clients (4B)) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 10.6s #peers 5 #RPCs 7555 #Ops 1399
--- PASS: TestManyPartitionsManyClients4B (10.55s)
=== RUN TestPersistOneClient4B
Test: restarts, one client (4B restarts, one client 4B ) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.5s #peers 5 #RPCs 5153 #Ops 1001
--- PASS: TestPersistOneClient4B (6.53s)
=== RUN TestPersistConcurrent4B
Test: restarts, many clients (4B restarts, many clients) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.4s #peers 5 #RPCs 5877 #Ops 1137
--- PASS: TestPersistConcurrent4B (6.43s)
=== RUN TestPersistConcurrentUnreliable4B
Test: restarts, many clients (4B restarts, many clients ) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.9s #peers 5 #RPCs 1596 #Ops 227
--- PASS: TestPersistConcurrentUnreliable4B (7.87s)
=== RUN TestPersistPartition4B
Test: restarts, partitions, many clients (4B restarts, partitions, many clients) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 14.4s #peers 5 #RPCs 6681 #Ops 1195
--- PASS: TestPersistPartition4B (14.39s)
=== RUN TestPersistPartitionUnreliable4B
Test: restarts, partitions, many clients (4B restarts, partitions, many clients) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 12.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 2253 #Ops 307
--- PASS: TestPersistPartitionUnreliable4B (12.15s)
=== RUN TestPersistPartitionUnreliableLinearizable4B
Test: restarts, partitions, random keys, many clients (4B restarts, partitions, random keys, many clients) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 12.2s #peers 7 #RPCs 5470 #Ops 576
--- PASS: TestPersistPartitionUnreliableLinearizable4B (12.23s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/kvraft1 95.729s
Part C: Key/value service with snapshots #
这一部分的目的是把 Snapshot 功能加上去.
这个时候就发现了一个问题, 刚才能通过 Part B 的代码反而跑不过 Lab 3D 的测试了.
仔细分析了一下原因, 问题应该是出在这里:
「在 Leader 机器执行 Put 请求的时候, 其 Raft 模块应该在接到请求以后立即广播一个 AppendEntities 而不是等下一次心跳的时候再广播. 否则会造成不必要的等待导致 Put 速度过慢」
在添加这个之前, Leader 向其他节点发送 AppendEntities 的时间间隔都是固定的, 但是加了这个之后再考虑 Snapshot 有可能会导致发送的 AppendEntities 响应出现乱序抵达的问题.
解决的方法就是每次发送心跳的时候都忽略掉之前发送的心跳. 我的解决方法是加了个时间戳用来指代当前发送的 AppendEntities 与 Snapshot 的次序, 如果 RPC 响应的时候时间戳小于心跳的时间戳, 那么说明这个 RPC 已经过时了, 应该忽略.
除了这个以外还踩了一个坑, 为了检查是否需要 Snapshot 在 rsm 的读取协程中添加了检查 raft 大小并创建 Snapshot 的逻辑. 但是发现这个逻辑会一直抢占锁. 因此需要修改一下, 只有执行过 DoOp 之后才允许创建 Snapshot. (不然的话, 因为日志都没 Commit, 所以创建 Snapshot 也无法压缩空间)
运行结果
kvraft1 % go test -v -run 4C
=== RUN TestSnapshotRPC4C
Test: snapshots, one client (4C SnapshotsRPC) (reliable network)...
Test: InstallSnapshot RPC (4C) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 2.8s #peers 3 #RPCs 278 #Ops 63
--- PASS: TestSnapshotRPC4C (2.83s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotSize4C
Test: snapshots, one client (4C snapshot size is reasonable) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 9.0s #peers 3 #RPCs 2581 #Ops 800
--- PASS: TestSnapshotSize4C (8.98s)
=== RUN TestSpeed4C
Test: snapshots, one client (4C speed) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 11.5s #peers 3 #RPCs 3239 #Ops 0
--- PASS: TestSpeed4C (11.53s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotRecover4C
Test: restarts, snapshots, one client (4C restarts, snapshots, one client) (reliable network)...
... Passed -- time 6.9s #peers 5 #RPCs 1067 #Ops 179
--- PASS: TestSnapshotRecover4C (6.95s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotRecoverManyClients4C
Test: restarts, snapshots, many clients (4C restarts, snapshots, many clients ) (reliable network)...
info: linearizability check timed out, assuming history is ok
info: linearizability check timed out, assuming history is ok
info: linearizability check timed out, assuming history is ok
... Passed -- time 10.8s #peers 5 #RPCs 82409 #Ops 16381
--- PASS: TestSnapshotRecoverManyClients4C (10.80s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotUnreliable4C
Test: snapshots, many clients (4C unreliable net, snapshots, many clients) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 4.2s #peers 5 #RPCs 1441 #Ops 223
--- PASS: TestSnapshotUnreliable4C (4.23s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotUnreliableRecover4C
Test: restarts, snapshots, many clients (4C unreliable net, restarts, snapshots, many clients) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 7.7s #peers 5 #RPCs 1019 #Ops 129
--- PASS: TestSnapshotUnreliableRecover4C (7.66s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotUnreliableRecoverConcurrentPartition4C
Test: restarts, partitions, snapshots, many clients (4C unreliable net, restarts, partitions, snapshots, many clients) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 16.9s #peers 5 #RPCs 1583 #Ops 127
--- PASS: TestSnapshotUnreliableRecoverConcurrentPartition4C (16.92s)
=== RUN TestSnapshotUnreliableRecoverConcurrentPartitionLinearizable4C
Test: restarts, partitions, snapshots, random keys, many clients (4C unreliable net, restarts, partitions, snapshots, random keys, many clients) (unreliable network)...
... Passed -- time 12.4s #peers 7 #RPCs 4347 #Ops 440
--- PASS: TestSnapshotUnreliableRecoverConcurrentPartitionLinearizable4C (12.40s)
PASS
ok 6.5840/kvraft1 82.664s
参考资料 #
- Building a Distributed MapReduce System in Go https://medium.com/better-programming/building-a-distributed-mapreduce-system-in-go-a22a205f5a0
- The Raft Consensus Algorithm https://raft.github.io
- In Search of an Understandable Consensus Algorithm (Extended Version) https://raft.github.io/raft.pdf